Back pain is a common problem among middle-aged and elderly patients. A wrong lifestyle can lead to pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, diseases of the internal organs. A neurologist, orthopedist, nephrologist, and urologist can treat back pain, depending on the origin. It is difficult for a patient to determine the cause of unpleasant feelings and choose the right doctor. Therefore, you should first contact a therapist who will refer you to a specialist, depending on the symptoms, history and the results of research.
Classification
There may be back pain:
- Myofascial.
- It is nociceptive.
- Neuropathic.
- Psychogenic.
Myofascial painobserved during the so-called formation. trigger points in the back muscles. The trigger points are pea-like nodules that form when the muscles are constantly tense (simply unable to relax). Moreover, when one segment of muscle fiber is compressed, the others stretch. This affects the mobility of the muscle fiber: it is limited. The fiber itself is shortened and becomes denser.
Trigger points are caused by excessive muscle tension. In addition, excessive stress can occur not only due to excessive physical activity, but also due to prolonged stay in one position (for example, sitting at a computer). In addition, trigger points often occur with osteochondrosis.
Another factor that contributes to the formation of trigger points is the overstimulation of sarcomeres (basic contractile units with a protein complex). If there is excessive stimulation of the sarcomeres, they are always in a contracted state.
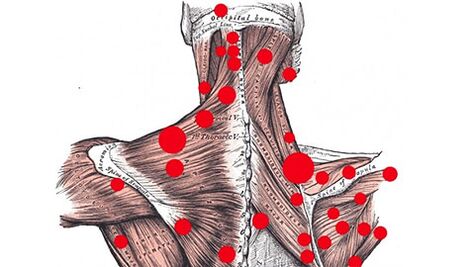
The presence of trigger points does not allow the muscle to relax completely. It begins to get tired quickly, even with small loads, shows excessive tension when moving, and recovers very slowly. Limited range of motion affects the entire facial chain. Other muscles and even some joints become less mobile.
Blood flow to the tissues surrounding the trigger point also suffers. For this reason, oxygen starvation is observed in this region. Rotten products accumulate, irritate the trigger point and therefore develop pain. In this case, the size of the muscle does not matter, it all depends on the degree of irritation of the point. Even the smallest muscle in the presence of trigger points can cause very unpleasant sensations.
A characteristic feature of myofascial pain is their reflection. This means that the pain is reflected in other parts of the body. It can occur in areas far away from trigger points. Thus, for example, pain under the shoulder blades or in the waist may develop due to the presence of nodules in the abdominal muscles. In addition, low back pain may occur due to trigger points in the calf area or thigh.
Myofascial pains are generally long-lasting and dull. Sometimes they are just moving, sometimes they are at rest. They can vary in strength: from minor discomfort to unbearable pain.
Nociceptive pain- The body's response to direct stimulation of pain receptors (nociceptors). In the posterior position, these are receptors located in the paravertebral ligaments, muscles, tendons, as well as in the articular capsules of the intervertebral joints and in the outer third of the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc. The patient may experience reflex muscle spasm, pain with dystrophic or pathological processes in the facet joints. The pain intensifies as you move.
Neuropathic paindevelopment of pathological processes in the nervous system: damage to the nerves or roots of the peripheral nervous system, disorders of the central nervous system. Such pain can be observed with osteoporosis, spondylolisthesis, hernias and spinal fractures. They intensify when bending, moving, straining, coughing, sneezing, and in most cases are transmitted to the limbs. Sometimes they are dull and painful, but more often they are sharp.
Psychogenic painoccurs due to muscle spasm caused by emotional stress, chronic stress or anxiety disorder.
In some cases, varieties can be combined with each other. For example, myofascial sensations coexist with nociceptive ones.
In addition, back pain is divided into 3 types:
- Acute (lasts less than 6 weeks).
- Subacute (6-12 weeks).
- Chronic (more than 3 months).
Acute / subacute painusually develops due to tissue damage (deep, superficial) due to cuts, wounds, inflammation. Thus, the body warns us that something is wrong. The pain passes after the tissues have completely healed.
Chronic painoccurs due to organ and system diseases or emotional disorders. If available, a thorough medical examination is required.
There may be pain depending on the location:
- Local.
- It was reflected.
- Radiation.
Local pain develops directly at the site of development of the pathological process. Reflected - if there are trigger points. Radiation - spreads along nerve fibers with damage to internal organs.
Why does my back hurt?
There are various causes of low back pain, including:
- Spinal curvature: scoliosis, kyphosis.
- Neurological diseases: herniated intervertebral discs, osteochondrosis, spondylosis, spondyloarthritis.
- Endocrine pathologies: osteoporosis.
- Respiratory system diseases: pleurisy.
- Pathologies of the kidneys and urinary system: urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis.
- Tumors.
Short-term pain (usually severe, burning) can have a variety of causes. These include:
- Damage.
- Excessive muscle tension (due to a monotonous posture or repetitive movements of the same type).
- Hypothermia.
Pain caused by degenerative processes occurs with the following diseases:
- Osteochondrosis.
- Intervertebral hernia.
- Intervertebral disc protrusion.
- Spondylosis deformities.
- Degenerative scoliosis.
- Osteoarthritis.
- Spondylolisthesis (displacement of the vertebrae).
- Spondylolysis (inconsistency of the spinal cord).
- Spinal stenosis.
Pain in the spine can develop due to diseases:
- Heart and large vessels: myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, aortic aneurysm.
- Lungs: cancerous tumors, pleurisy.
- Esophagus.
- Gallbladder and bile ducts: acute and chronic cholecystitis.
- Kidney and urinary tract.
- Pancreas.
In rare cases, back pain can be of infectious origin. For example, sometimes my back hurts from the flu. The infection can also penetrate the spinal cord in nearby organs: urinary tract, kidneys.
Other causes of back pain may include changes in hormonal levels (for example, age-related, during or after menopause). In this case, hormonal spondylopathy (degenerative changes in the spine) occurs
Back pain: what to do?
If you have a severe pain attack, be sure to see a doctor as soon as possible. But if the feelings are so strong that any action causes pain, first aid is needed. You should lie on your back on a flat, hard surface (such as a floor). This will help relieve spasms, relax muscles and reduce pain.
Do not sink on a flat surface and change the position of your back. Lie on your back and try to roll to the side. This will relax the spine. When the pain subsides, return to your back. It is recommended to put something by lifting it up under your feet. In this case, lie down for 10-15 minutes.
You also need to climb properly: first roll to you. Get up on all fours from this position. Then lean on something (if there is no support nearby - drag it towards him) and slowly get up. Only then carefully straighten your back.
Do not delay seeing a doctor to find out why your back hurts so badly. This will help prevent new attacks.
Diagnostics
If you have back pain, you must make an appointment with a therapist:
- appears during physical strength, muscle tension;
- Lasts more than 3 days;
- repeated episodically.
In the following cases it is necessary to consult a doctor immediately:
- back hurts constantly;
- an increase in body temperature, numbness of the limbs, muscle weakness in the morning are added to the pain;
- pain does not pass during sleep;
- more pains at night.
At the appointment, the doctor will collect a medical history, examine the patient (assess the condition of the skin, body condition and symmetry, gait, etc. ). Then the job will assign:
- general analysis of blood and urine;
- x-ray;
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging.
If necessary, the therapist will refer the patient to a neurologist, orthopedist, urologist, gynecologist or nephrologist.
Treatment of low back pain
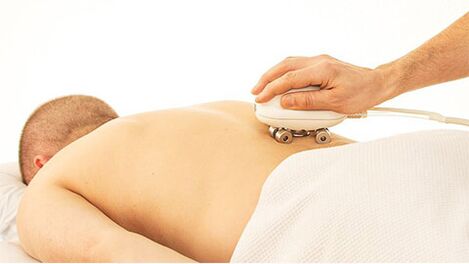
Treatment of low back pain is comprehensive and can include:
- take medication (anti-inflammatory, analgesics, restorative drugs);
- blockade (long-term analgesic);
- physiotherapy procedures;
- physiotherapy exercises;
- massages;
- treated by hand.
If conservative methods do not give the desired result, surgical treatment is prescribed. Modern methods allow you to perform low-traumatic precision operations with a short rehabilitation period.
Prevention of back pain
Simple preventative measures can help prevent back pain. Important:
- Control your posture.
- Lie on a bed with a firm mattress.
- It is necessary to engage in activities related to a long sitting position (driving, working on a computer), to change posture from time to time, as well as to arrange breaks and warm up.
- Lean on something while standing for a long time.
- Do not wear high heels for more than 2 hours in a row.
- Spend time on moderate physical activity (swimming, fitness).
- Keep track of your weight - back pain can occur due to the presence of extra pounds.
- Try not to lift weights.
- Do not turn or bend with sudden movements.
- Treat urological and gynecological diseases in a timely manner.
Annual preventive visits to the therapist will also be helpful. Pathologies identified in the early stages can be eliminated without waiting for the development of complications.






















